Ceylon Cinnamon
Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume
Family: Lauraceae
Cinnamomum species endemic to Sri Lanka including the two cultivars of
C. zeylanicum released by the Department of Export Agriculture, Sri Lanka
History of Ceylon Cinnamon
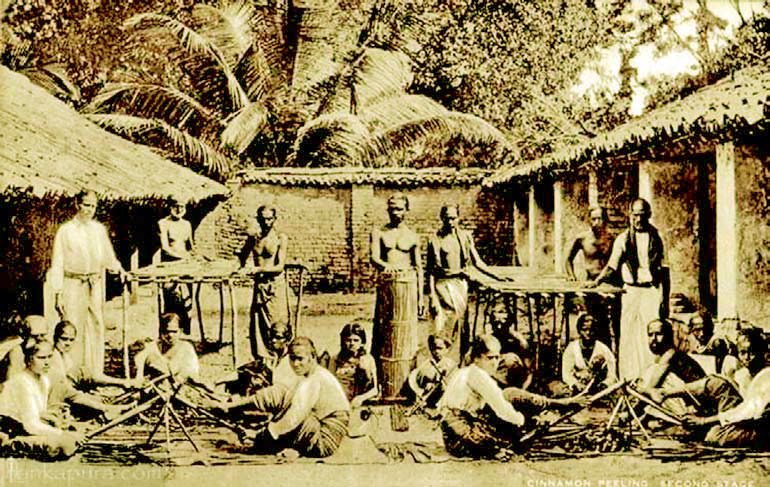

Cinnamon, derived from the dried bark of the Cinnamomum zeylanicum tree, is native to Sri Lanka and has a history dating back to around 2800 B.C., where it was referenced as “kwai” in Chinese texts. It is mentioned in the Bible and was used by ancient Egyptians for embalming due to its pleasant odor and preservative qualities. During the 14th and 15th centuries, cinnamon became a precious spice in the West, primarily for preserving meat. The quest for cinnamon spurred global exploration in the 15th century when it was exclusively produced in Sri Lanka.
Portuguese traders arrived in Ceylon during this time, enslaving locals and taking control of trade from Arab merchants. The Dutch later displaced them, enhancing production through domestication and expanding cultivation along coastal areas. After the British takeover in 1815, the cinnamon trade declined due to rising tea and rubber plantations.
The most significant historical document regarding the Sri Lankan Cinnamon trade is the Up Country-Dutch Agreement (Hanguranketha Agreement), signed on February 14, 1766, allowing the Dutch to harvest Cinnamon while agreeing to protect Sri Lanka from foreign invasions. With years of experience in the industry, our company has established a strong reputation for excellence and reliability. We have a proven track record of delivering outstanding results and have helped countless individuals achieve their dreams. Our commitment to continuous learning and innovation ensures
With years of experience in the industry, our company has established a strong reputation for excellence and reliability. We have a proven track record of delivering outstanding results and have helped countless individuals achieve their dreams. Our commitment to continuous learning and innovation
Products and Uses
Within the body of your blog post lies the heart of your message. Break down your content into coherent sections, each with a clear heading that guides readers through the narrative. Dive deep into each subtopic, providing valuable insights, data, and relatable examples. Maintain a logical flow between paragraphs using transitions, ensuring that each point naturally progresses to the next. By structuring your body content effectively, you keep readers engaged and eager to learn more.
Varieties

Sri Lanka is home to eight Cinnamon species, but only Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume is grown commercially. Traditionally, cinnamon was categorized by bark taste: “Pani-Miris Kurundu” was the best with a sweet-pungent flavor, followed by “Miris Kurundu,” “Sevel Kurundu,” and “Thiththa Kurundu.” Currently, ten accessions have been identified for yield and quality, with two lines—“Sri Vijaya” and “Sri Gamunu”—having been released; others are under evaluation in various agro-climatic zones.
**Geographical Indication (GI) for Ceylon Cinnamon:**
A geographical indication (GI) signifies products with specific origins that possess unique qualities or reputations tied to that origin. On February 2, 2022, Sri Lanka received its first GI certification from the European Union for Ceylon Cinnamon. This achievement marked a significant milestone following a decade-long effort led by the Sri Lanka Export Development Board (EDB) under the Ministry of Trade, supported by public and private stakeholders.
Major Growing Areas In Sri Lanka
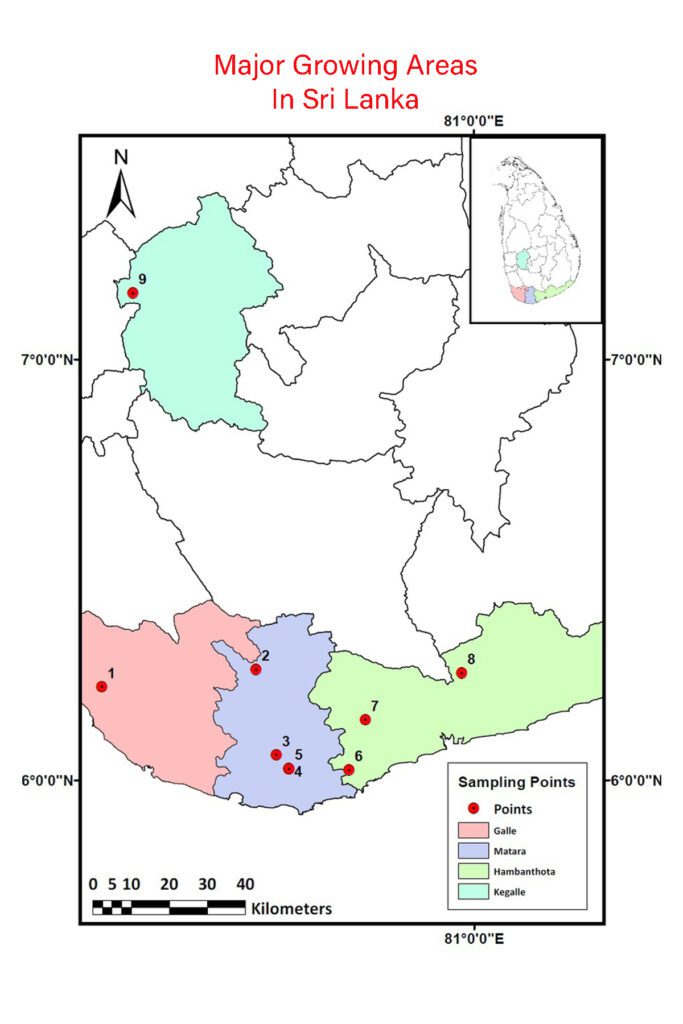
Cinnamon seems to have originated in the central hills where seven wild species of cinnamon occur in Kandy, Matale, Belihull oya, Haputale, Horton planes and the Sinharaja forest range. Presently cultivation concentrated along the coastal belt from Negambo to Matara, it has also made inroads to Kalutara and Ratnapura.
There are two main type of Cinnamon in the World
- Ceylon cinnamon: This type is also known as “true” Cinnamon.
- Cassia cinnamon: This is the most common variety today and what people generally refer to as “cinnamon.”
Cinnamon is made by cutting the stems of cinnamon trees. The inner bark is then extracted and the woody parts removed.
When it dries, it forms strips that curl into rolls, called cinnamon sticks. These sticks can be ground to form cinnamon powder.
The distinct smell and flavor of cinnamon are due to the oily part, which is very high in the compound cinnamaldehyde
CEYLON CINNAMON VS CASSIA
Ceylon Cinnamon is considered to be the most delicate among the major species of cinnamon. Its flavor is more subdued, less bitter, and has a sweet finish. It has a sweet aromatic smell. Whereas, cassia shares a strong, spicy-sweet flavor, and aroma. Its flavor is extremely bitter when compared to true cinnamon. It produces a burning aftertaste once consumed.


(Picture Copyright-EDB Sri Lanka)
The difference between Ceylon and Cassia Cinnamon can be summarised as below
| Ceylon Cinnamon | Cassia Cinnamon | |
| Colour | Light brown | Reddish dark brown |
| Formation | Several layers of fold like a cigar | One inward fold with an empty cavity |
| Texture | Soft and fragile. Easy to break | Hard and rough. Difficult to break |
| Flavour & Aroma | Sweet flavor. Soft aroma | Pungent & zesty flavor. Strong aroma |
| Composition | 0.004% of Coumarin | 5% of Coumarin |
| Use | Safe for prolonged use. Has antioxidant and antimicrobial qualities | Causes liver damage by constant use. |
| Origin | Sri Lanka | China, India, Vietnam, Indonesia |
| Availability | Expensive. Used in the EU, Western Asia, Oceania | Low priced. Used in Canada and the USA |
Grade of Ceylon Cinnamon
Mainly Ceylon Cinnamon is categorized into 4 major grades, They are Alba, Continental, Mexican, and Hamburg. This is based on the diameter of the cinnamon sticks(quills), Most expensive grade is Alba.
Alba is the highest quality. Alba has a sweet taste, pleasant aroma and slender appearance. exquisite aroma and rich flavor. Alba has a tan color with the diameter of the quills ranging from 6-8mm.
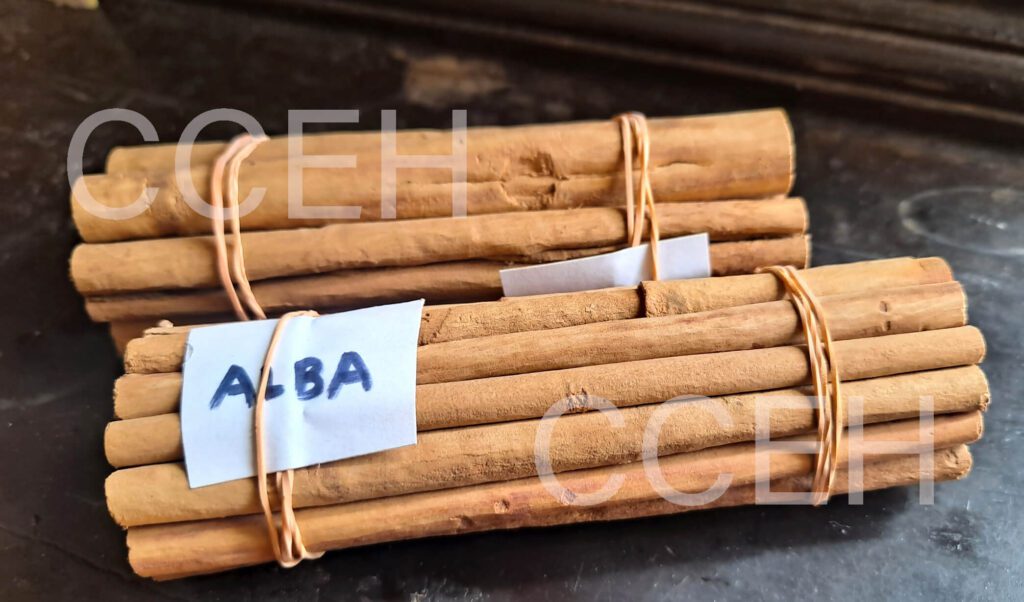
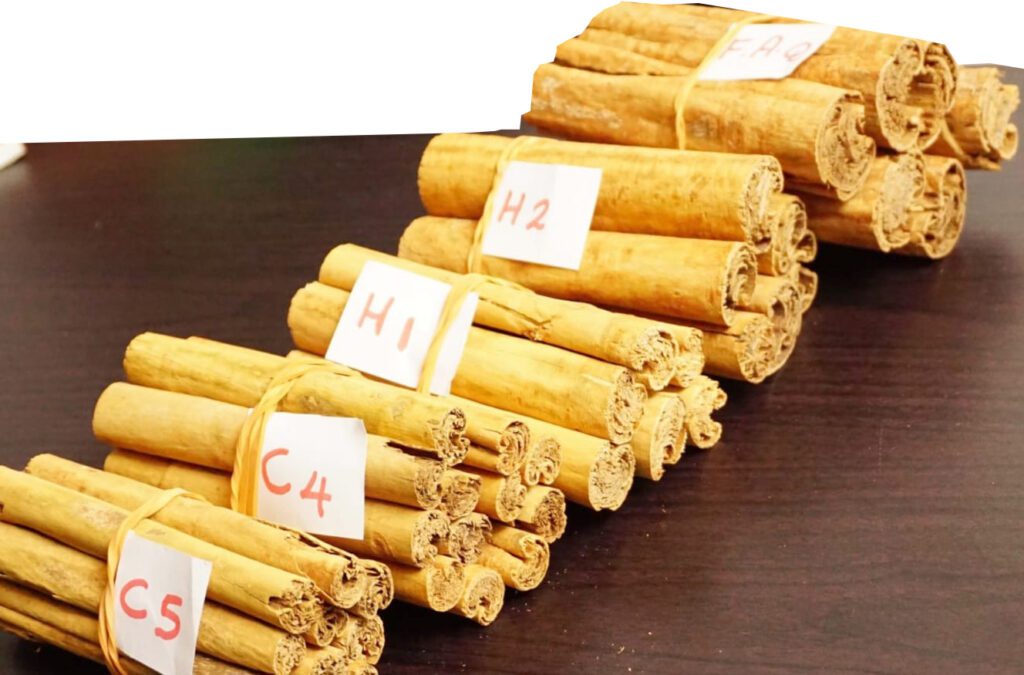


Specifications for cinnamon quills
| Grade | Diameter (max. mm) | Min. no. of 42”long quills per kg | % rough quills per kg |
| Alba | 6mm | 45 | – |
| Continental- C/Extra Special-(CESP) | 8mm | 33 | 19 |
| C5 Special | 9mm/10mm | 30 | 10 |
| C5 | 12mm | 27 | 15 |
| C4 | 16mm | 22 | 15 |
| C3 | 18mm | 20 | 20 |
| C2 | 19mm | 18 | 20 |
| Mexican (M) | |||
| M5 Special | 16 | 22 | 60 |
| M5 | 16 | 20 | 60 |
| M4 | 19 | 18 | 60 |
| Hamburg (H) | |||
| H1 | 23 | 11 | 25 |
| H2 | 25 | 9 | 40 |
| H3 | 37 | 7 | 60 |
Cinnamon (Chips/Bale/Cut)
BALE Max, Length Of Stick Is 42 cm. Bale Packed Form Of Compact Bales About 25 kg to 45 kg Wrapped With Suitable Material (Gunny Or Pp Bags) CHIPS Dried Bark of Unpeelable Cinnamon Stems, Branches and Trimmings Inclusive of The Outer Bark Which Has Been Obtained By Chipping Or Scrapping Consist of Well Dried, Hand Pick And Clean Unpeeled Cinnamon Bark. CUT Cinnamon Cut to a Required Length And It’s Graded Based on Diameter. Cut Grades: CS/C5/C4/MS/H…
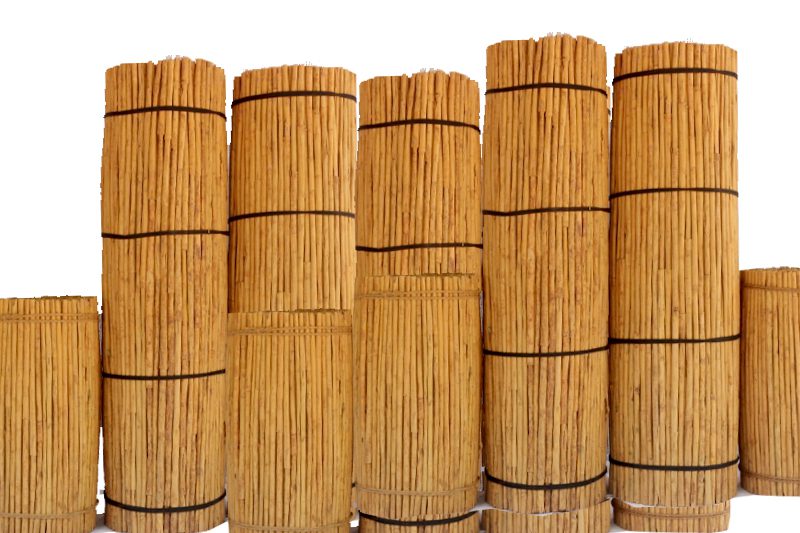

Bale
Ceylon Cinnamon Oil
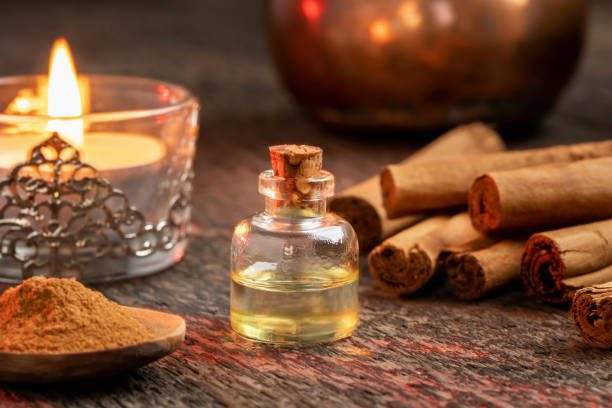

Made with the leaves, twigs, and bark of the Ceylon Cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum) or true cinnamon tea, Ceylon Cinnamon Essential oil is available in the form of cinnamon bark oil and cinnamon leaf oil.
Extracted through steam distillation, the essential oils vary in colour yet have a sweet, spicy, slightly woody, and clove-like aroma. The chemical compounds in the oil include Cinnamaldehyde and Eugenol as well as cinnamic acid and cinnamyl acetate.
The chemical compounds provide Ceylon Cinnamon Oil with antifungal, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-diabetic properties making it a widely used ingredient in many industries.
Health benefits of Ceylon Cinnamon Oil
- Eugenol in Ceylon Cinnamon Oil delivers strong antibacterial and antifungal properties while its antidiabetic and antioxidant properties help to reduce blood sugar level and blood pressure.
- Improves oral health
- Reduces and soothes skin irritation and eczema
- Reduces acne and blemishes
- Helps to Reduce Blood Glucose Levels
- Helps weight loss
Uses of Cinnamon Oil
- An ingredient in household cleaning products, insect repellents, and disinfectants
- An ingredient used in oral care products
- Used as a preservative and a flavoring in the food industry
- Used in aromatherapy to reduce depression, anxiety, and exhaustion and to stimulate libido and boost immunity.
- An ingredient personal care products including lotions, cleaners and shampoo
- A massage oil that relieves joint pains and strains


