Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume
Family : Lauraceae

Colonial oppression
Cinnamon was widely consumed as early as 3000 BC. The ancient world considered it a luxurious spice. For ancient Egyptians, Cinnamon was a status symbol, which they also used in perfumes. The Greeks considered it a medicine. Sinhalese literature in the 10th century mentions that the island’s cinnamon was highly valued. In the 13th century, Sinhalese kings established economic ties with Egypt to export it. Historian Nirmal Ranjith Dewasiri says that from the beginning of the 10th century, Arab merchants traded Sri Lanka’s Cinnamon to Europe along with other spices; the island became an important hub in the Indian Ocean trade.
In ancient Sri Lanka, the king was considered the guardian of the land. For cultivating the land, people had to perform a service to him. Historically, these tasks were assigned to certain castes. Cinnamon peeling was reserved for the Salagama community, who were originally weavers and believed to be the descendants of post-13th century South Indian migrants.
Cinnamon grew in the wild in Sri Lanka. Therefore, for months of the year, the head of the household would set off to the jungles to produce a certain amount of cinnamon for the king, in return for the land they cultivated. The main Ceylon Cinnamon growing areas are Matara, Galle, Kalutara, Ratnapura, and Gampaha areas in Sri Lanka. Mainly in the coastal belt.
Then in 1658, the Dutch (allied with the Kandyan kingdom in Sri Lanka) took control of Sri Lanka’s coastal belt after a series of battles with the Portuguese and established a cinnamon monopoly by exploiting the Salagam community to supply the spice to meet the growing demand of the European market. By 1794, there were 609 million cinnamon trees in southwest Sri Lanka. “By the end of the Dutch rule, there were massive commercial plantations of cinnamon along the coast. When the British occupied the island in 1815, other cash crops like coffee and tea became more important,” referring to Dutch-era plantations like Cinnamon Gardens in Colombo. Today, there is hardly a cinnamon tree left in the area, which is now an upmarket neighborhood with residential houses, boutiques, and cafes.
What variety is Ceylon cinnamon?
There are eight cinnamon species in Sri Lanka. Among them only Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume is grown commercially. In tradition, there were several types of cinnamon categorized based on taste of the bark. “Pani-Miris Kurundu” was the best with sweet-pungent taste and “Miris Kurundu”, “Sevel Kurundu” and “Thiththa Kurundu” are the others. Currently ten cinnamon accessions have been identified based on yield and quality performances and best two lines, named as “Sri Vijaya” and “Sri Gamunu”, were released. Other selections are under evaluation in different agro climatic zones.

Medicinal and Chemical Properties
Cinnamon essential oil Bark contains about 65%–80% of cinnamaldehyde and 5%–10% Eugenol. While cinnamon leaves constitute of eugenol as major ingredient with the concentration varying from 70% to 95% and cinnamaldehyde about 1%–5% (Rao and Gan, 2014)
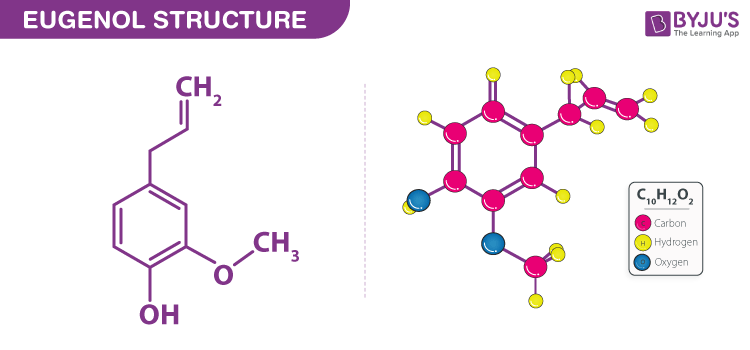
Eugenol is the main chemical ingredient in cinnamon leaf oil and Cinnamaldehyde is present in cinnamon bark oil. However, there are hundreds of minor chemical ingredients that give characteristic flavor and aroma to true cinnamon.
Cinnamon has been used for medicinal purposes and has been known as a healing herb since it is mentioned in Chinese botanical books that date back to 2700 B.C. In ancient Rome It had been used medicinally for cold and flu as well as for the problems of the digestive system. Recently, it has been studied for its ability to boost brain power, reduce blood clotting and its healing effects on the heart and colon. Recent studies have proved its ability to control type 2 diabetics by reducing blood sugar level and to reduce blood cholesterol level. In traditional society’s cinnamon is said to have used to relieve digestive upset, congestion, menstrual problems, stiff joints and muscles. It has said to been used as an anti-inflammatory agent and as a pain reliever to arthritis patients. Some studies had shown that cinnamon help to cure urine tract infections and to fight tooth decay and gum disease.
